No matter what kind of business you’re in, the threat of cybercrime — and its associated costs — looms large. According to IBM Security, globally the average cost of a single breach reached an all-time high in 2023 ($4.45 million). In the U.S., that number is even higher, with an average cost of $9.48 million per breach, an increase of 0.4% from last year.
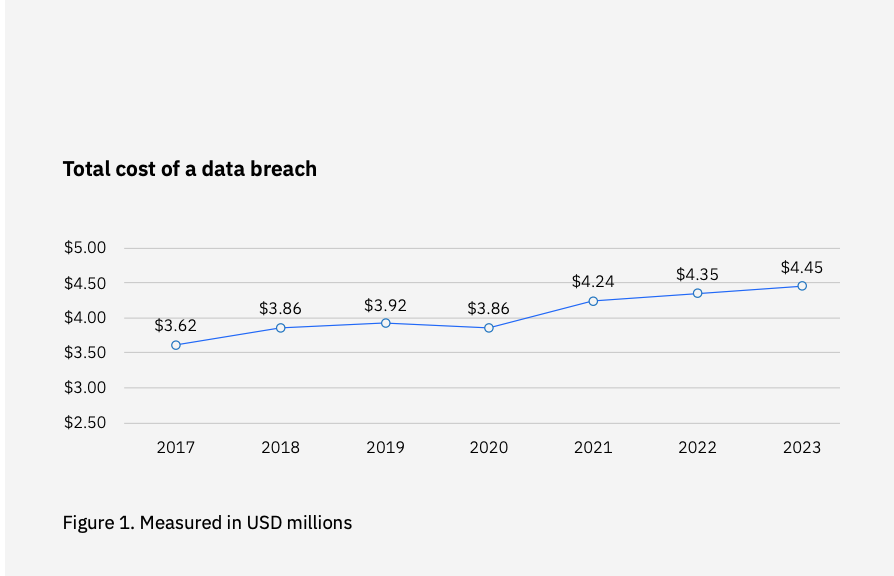
Source: IBM Security’s Cost of a Data Breach Report 2023
More than ever before, rigorous cybersecurity measures — including appropriate cyber insurance coverage — are critical for businesses to protect themselves and their customers. However many businesses, particularly those in the small to medium-sized range, continue to hold onto misconceptions about cybercrime and cyber insurance that might be preventing them from taking appropriate action.
In this article, we’ll dispel some of these common myths and call attention to the importance of cyber coverage when it comes to safeguarding your business from a breach or attack.
Myth #1: We’re Too Small to Be a Target
One of the most prevalent misconceptions is the belief that cybercriminals only target large corporations. This couldn’t be further from the truth. An estimated 74% of small and medium-sized businesses fell victim to cyberattack in 2022. Cybercriminals often view small and medium-sized businesses as easy and lucrative targets. They assume these businesses lack robust cybersecurity measures, making them vulnerable to attacks.
In reality, size does not determine susceptibility to cyber threats. All businesses are at risk, and having cyber insurance is a wise investment in protecting a company’s assets and reputation. Appropriate cyber coverage can help manage the costs of recovering from an attack, including legal fees, notification expenses, and reputational damage control, which — in extreme circumstances — can be a death sentence for smaller organizations.
Myth #2: We Have Strong Cybersecurity, So We Don’t Need Insurance
While having strong cybersecurity measures in place is essential, it’s important to understand that no system is ironclad. Furthermore, cybercriminals are constantly adapting and using more sophisticated or unexpected methods to identify and exploit vulnerabilities. Cyber insurance should be viewed as a critical complement to robust cybersecurity efforts. It offers financial protection in the case of a data breach, despite your best efforts to minimize the risk. Additionally, cyber insurance policies often include value-added services such as incident response guidance to help organizations mitigate the damage and recover more quickly.
Myth #3: Our Commercial General Liability Insurance Covers Cyber Incidents
This is a common, and potentially costly, misunderstanding. General liability insurance typically does not cover cyber incidents, as it’s designed for different types of risks, such as bodily injury or property damage. Cyber insurance is specifically tailored to address the unique challenges posed by data breaches, cyberattacks, and other digital threats. Although some general liability policies may include cyber coverage, the coverage tends to be limited and insufficient to fully cover the cost of a breach or attack. With a standalone cyber policy tailored to the specific needs and risks of a business, the organization’s leadership can rest assured the company won’t be left exposed and financially vulnerable.
Myth #4: Cyber Insurance Is Too Expensive
Some small and mid-sized business owners doubt (or misunderstand) the value of cyber coverage and are reluctant to allocate funds during annual budget planning. In reality, the cost of cyber insurance is often much lower than the potential expenses resulting from a data breach or cyberattack. According to the 2023 IBM Security report, the average cost of a data breach in 2023 for organizations with fewer than 500 employees is a staggering $3.1 million (a 13.4% increase from 2022). The cost of a single data breach can be catastrophic for a small business, after tallying up legal fees, customer notification costs, reputational damage, and lost revenue from downtime. Cyber insurance can provide the financial safety net needed to recover from such incidents.
Myth #5: We Don’t Need Insurance If We Don’t Store Sensitive Customer Data
Most companies store some sort of sensitive customer data — names, addresses, payment details, etc. But even if a business is confident that it doesn’t store that type of data, the organization still may be at risk from other types of cyberattacks. A phishing attempt, for example, might trick unsuspecting employees into divulging a company’s banking information or willingly transferring large sums of money to a cybercriminal’s account. A ransomware attack could result in critical business software or systems being held hostage in exchange for payment of an exorbitant ransom. Cyber insurance can provide coverage for these potential threats, ensuring that the business can recover quickly and continue to operate smoothly.
Myth #6: Our IT Team Can Handle Cybersecurity
A corporate IT team is an invaluable part of a company’s defense against cyber threats, but they likely have other responsibilities vying for their attention and time. They also may not have the bandwidth to stay on top of every new and emerging cyber threat. Cyber insurance companies don’t just provide financial protection; they may also offer access to experts who can assist with breach response and recovery efforts. This additional support can make a significant difference in proactively addressing vulnerabilities and, should an attack occur, minimizing any damage and downtime.
Myth #7: We Can’t Be Held Responsible for Someone Else’s Actions
Some business owners mistakenly believe they can’t be held legally or financially responsible for the actions of hackers who breach their systems. However, businesses have legal and financial responsibilities to protect customer and employee data. Data breach regulations and privacy laws often require businesses to notify affected parties, investigate the breach, and potentially pay fines and face legal actions. Cyber insurance helps mitigate the financial impact of these obligations and ensures businesses can stay compliant with data protection laws.
Myth #8: We Don’t Have to Worry About Data Backups — Our Software Providers Do That Automatically
Many businesses assume that data protection is solely the responsibility of their software providers. They believe these third parties will back up data and ensure data security on their end — and this may be true to some extent. However, this kind of thinking neglects the importance of the business maintaining control over its proprietary data. While third-party providers may offer data backup services, it’s essential for organizations to create a data backup strategy and take an active role in safeguarding sensitive information. The in-house IT team should know what’s being backed up, how often, and where it’s being stored. As part of their risk-mitigation packages, cyber insurance programs often provide companies with vendor recommendations that can assist with setting up proper data backup systems and provide guidance on best practices.
Cyber Insurance for Small and Medium-Sized Businesses
Cyber insurance is a vital component of a cyber risk management strategy for small and mid-sized businesses. Insurance provides financial protection, access to expert support, and peace of mind in a world that increasingly relies on digital data. Don’t let these common myths and misconceptions prevent you from taking the necessary steps to safeguard your client’s business.
MiniCo’s Cyber Insurance program is tailored specifically to the needs of small and medium-sized businesses. Our coverage includes everything from breach response to business interruption loss, as well as data recovery costs, privacy regulatory defense and penalty costs, and more. Visit our Cyber Insurance program page for coverage details and to get a quote.



